In graph theory, the line graph of a given graph G, denoted as L(G), is a graph that represents the adjacency relationships between the edges of G. Specifically, L(G) contains one vertex for each edge in G, and two vertices in L(G) are considered adjacent if and only if their corresponding edges in G share a common vertex*.
Construction of L(G) from G:
The transformation from G to L(G) follows a systematic procedure to preserve the structural relationships between edges while redefining them as vertices. The steps for constructing L(G) are outlined below:
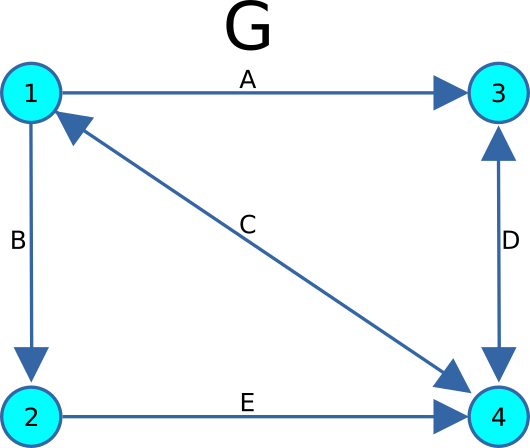
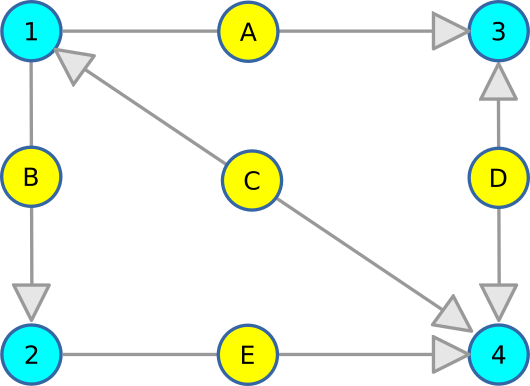
For each edge present in G, a corresponding vertex is introduced in L(G), ensuring that every edge in the original graph is represented as a distinct node in the transformed line graph.
*J. L. Gross and J. Yellen, Graph Theory and Its Applications. 2005.

